閱讀及使用開放數據的實用指南 (請參考英文版)
Introduction
Open Data is information that is freely and easily accessible, usable, and shareable by anyone. Most of the Open Data is machine readable format, including XML, JSON and CSV.
Get the Open Data
- Get the Open Data from Open Data Portal (https://data.gov.hk) or HKCSDI Portal (https://portal.csdi.gov.hk/csdi-webpage/)
- Search for the Open Data you need.
- Based on the file format, select the suitable tools.


To use, analyze, and innovate with this data, you can use the following tools:
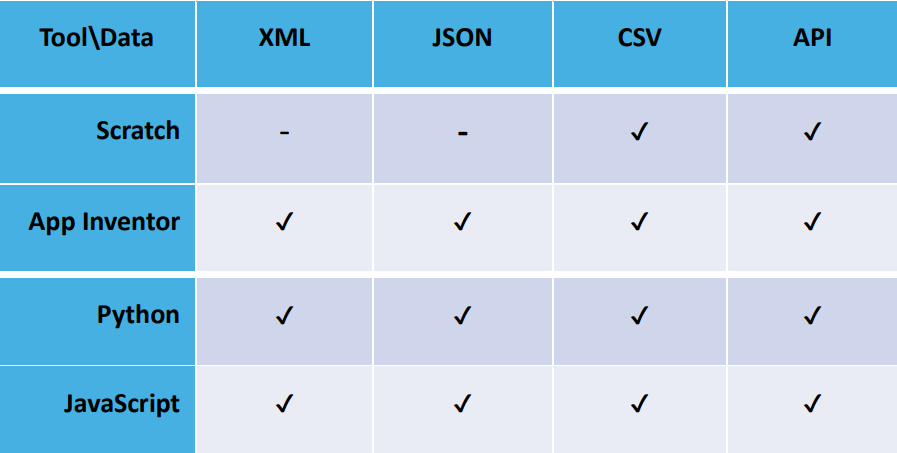
(Table 1: Tools to read Open Data)
Following we will introduce how to get the data, read and display open data with different tools.
Prepare the Data
Downloadable Data (XML, JSON, CSV)
For Open Data in format XML, JSON and CSV, if it is downloadable, you can download the data and use them directly.
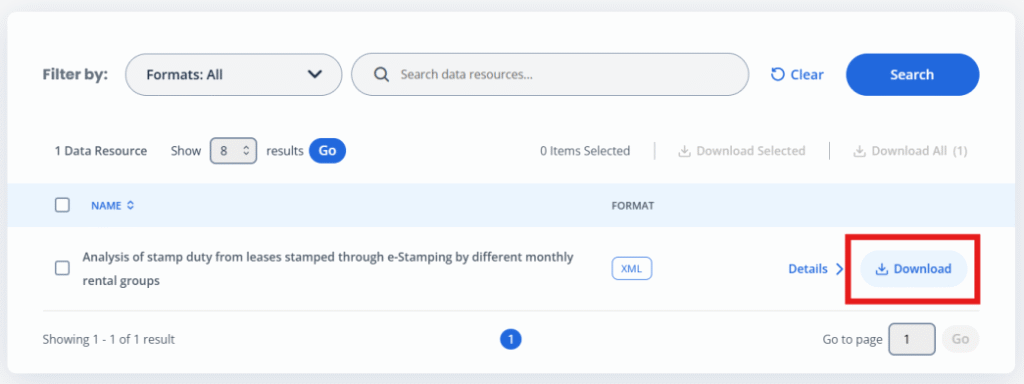
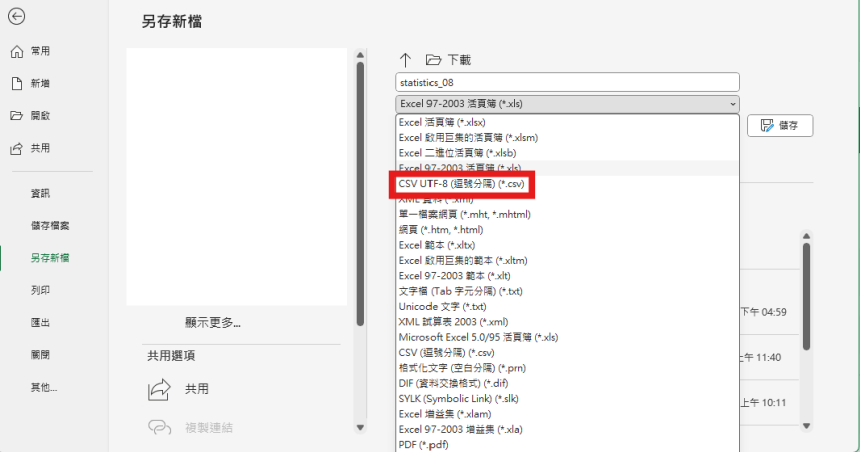
Downloadable Data (XLS)
1. Download the open data in XLS format.
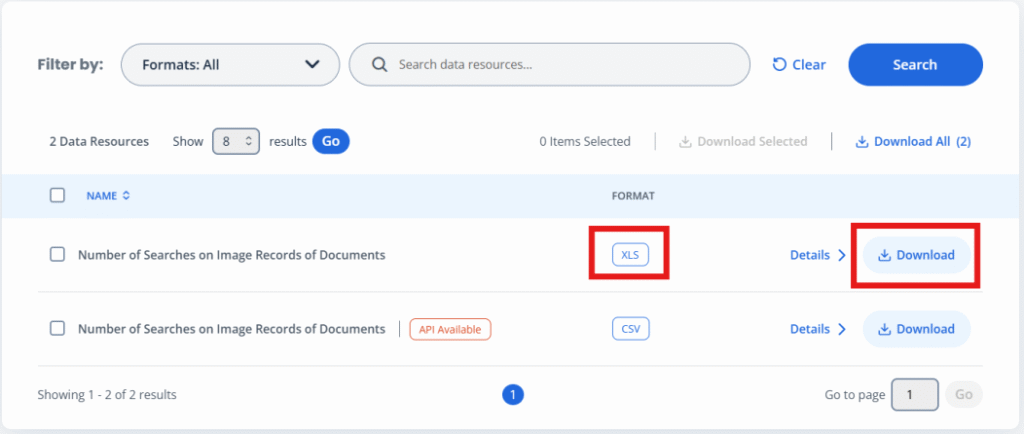
2. Open the file and save as .csv format.
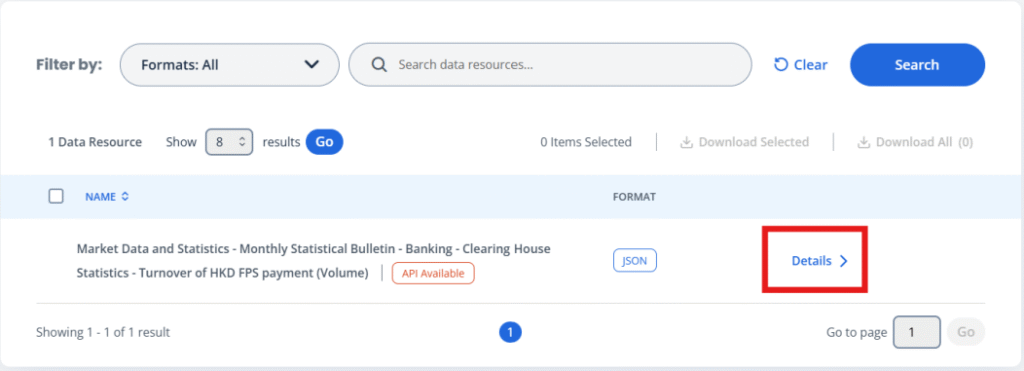
Non-downloadable Data (API)
1. Check the data resource details of the API.
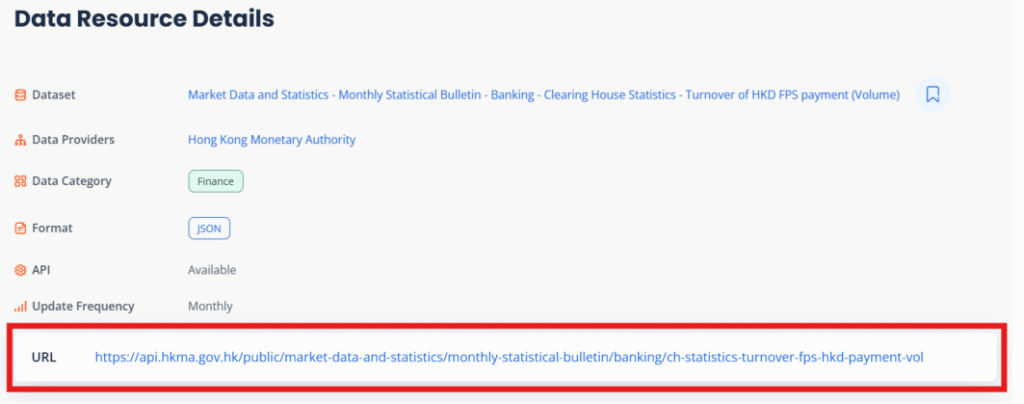
2. Get the API link from the URL.
Scratch
Scratch with CSV
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-cr-crdata-stat-company-searches
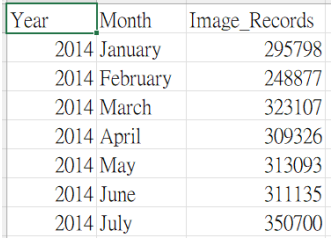
(Data Sample)
1. Go to Scratch Website (https://scratch.mit.edu/)
2. Create Project directly by clicking “Create” button.
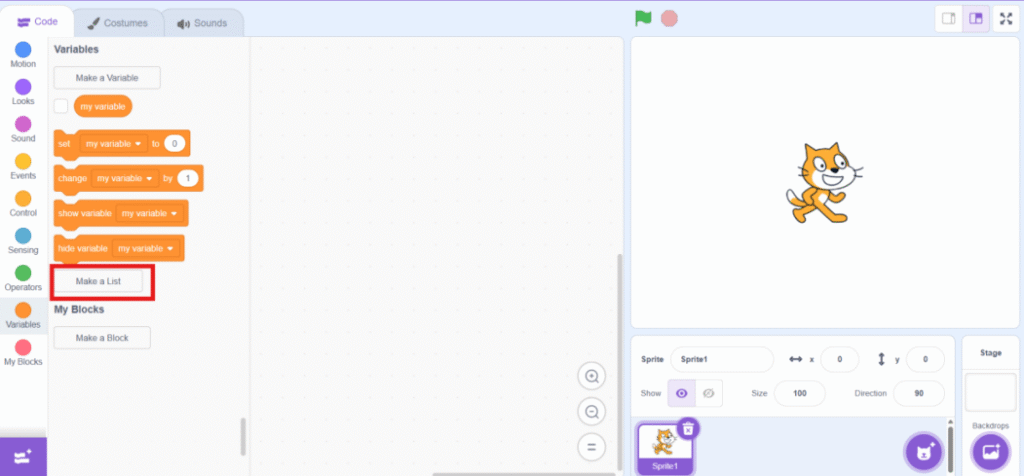
3. To read the CSV file, you need to make a list under “Variable” category.
4. Make a list for each column you need to use.
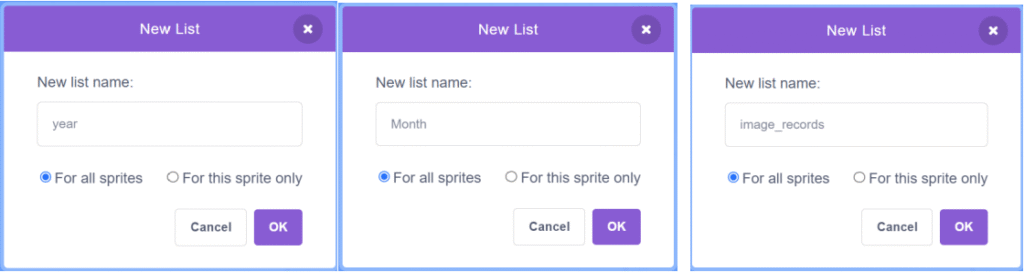
(Create three lists for three column)
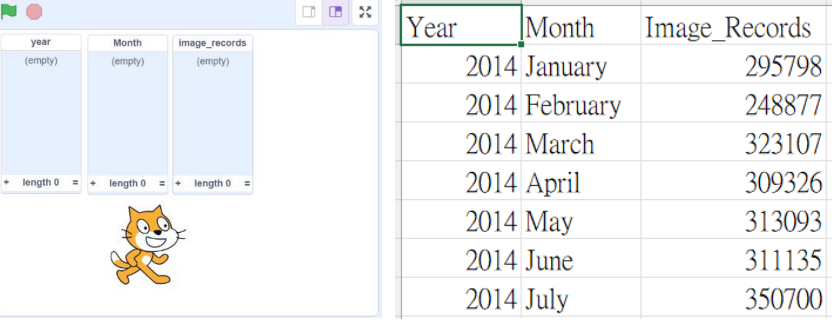
5. Right click on the list and import the open data.
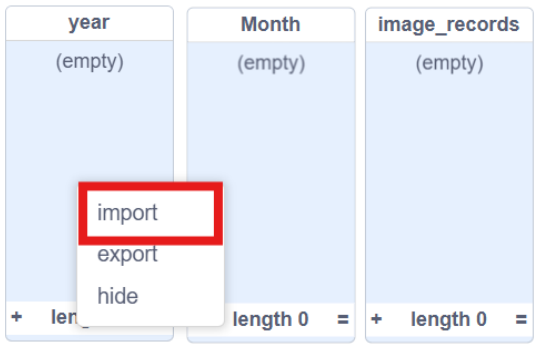
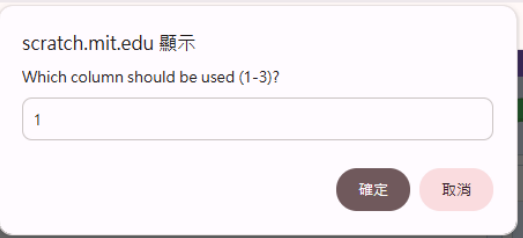
6. Type the column number you want to import. In the sample data, Column 1 is “Year”.
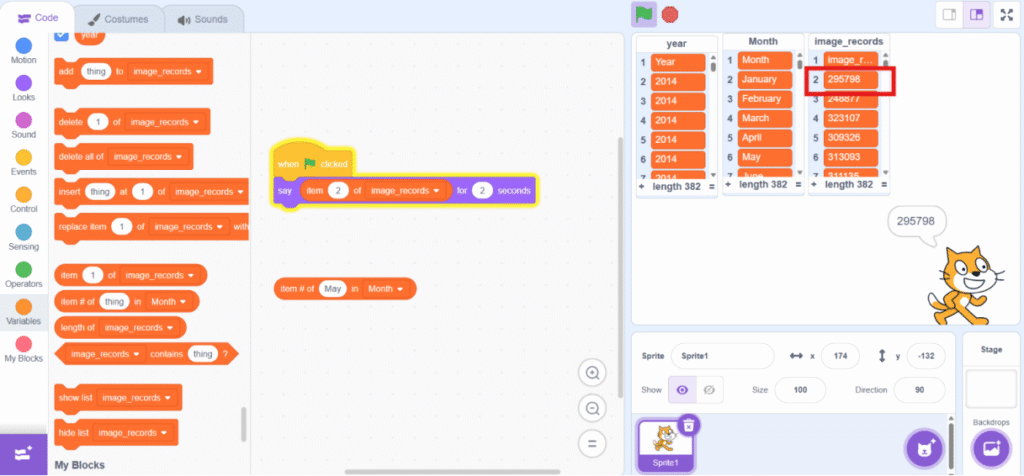
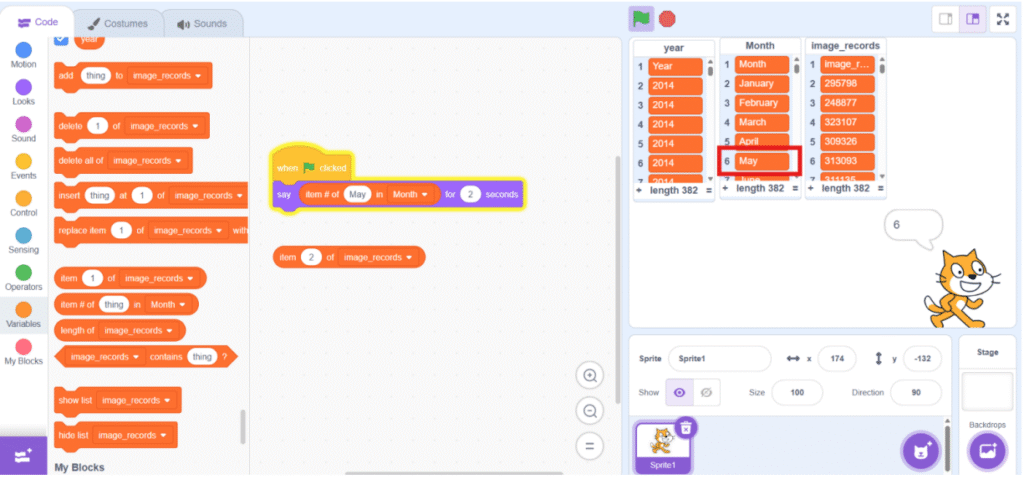
7. Get the data using blocks under “Variable” category.
Scratch with API in JSON format
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-hkma-t03-t031203ch-statistics-turnover-fps-hkd-payment-vol
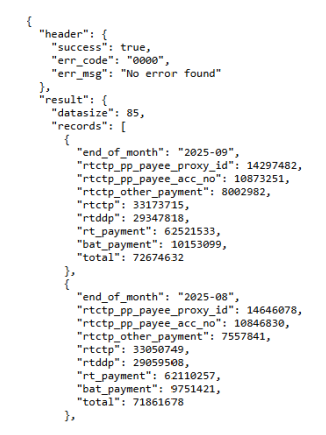
(Data Sample)
1. Go to Scratch with special Extension (https://osep-scratch.github.io/app/app/)
2. Go to “Extension”.
3. Add “JSON” extension to the project.
4. Get the JSON data using block in “JSON” category.
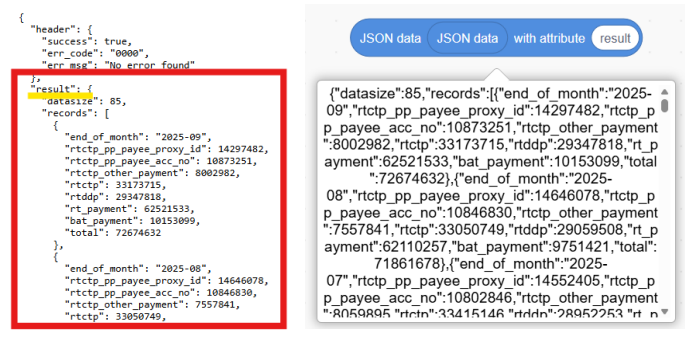
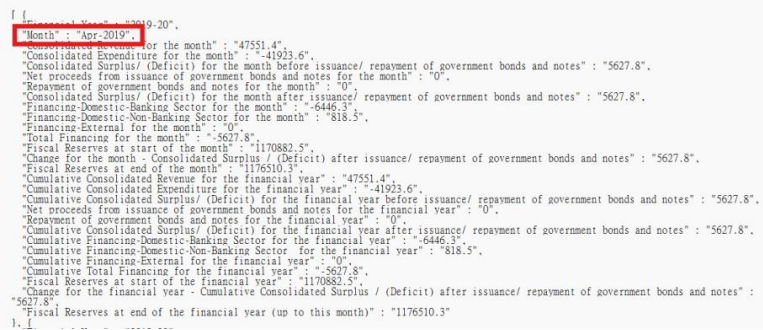
5. Get the targeted data with block. For example, if you want to get the “end_of_month” of the first record:
a. Get the data with attribute of the 1st layer.
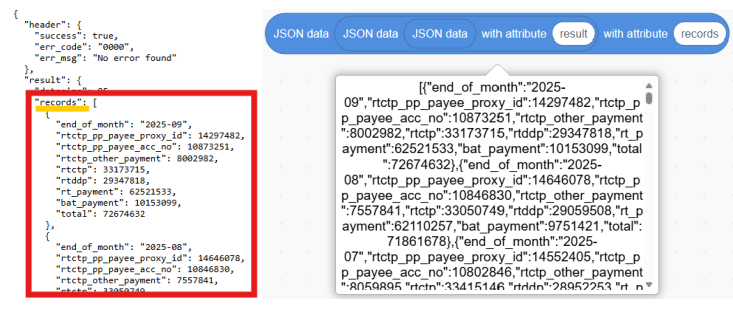
b. Get the data with attribute of the 2nd layer.
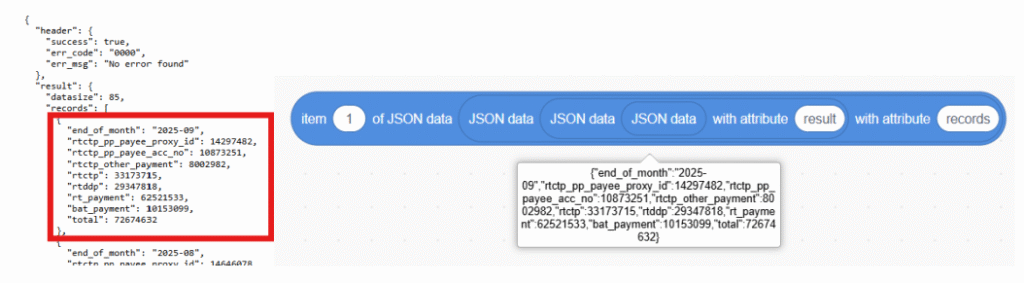
c. Get the first data of the “records” list.
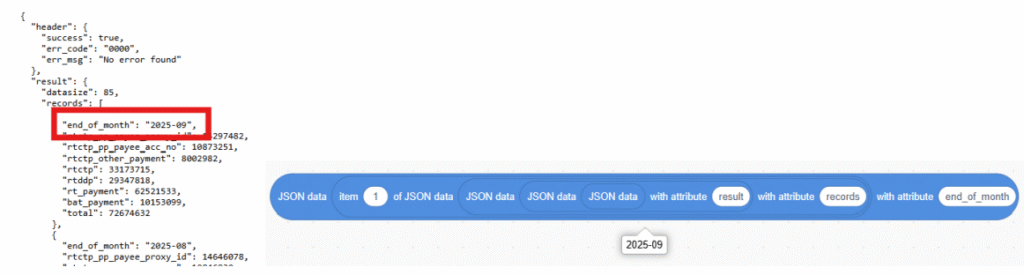
d. Get the data with targeted attribute “end_of_month”
App Inventor
App inventor with XML
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-ird-ird_json-stamp-lease
1. Login and create a new project in MIT App Inventor (https://appinventor.mit.edu/).
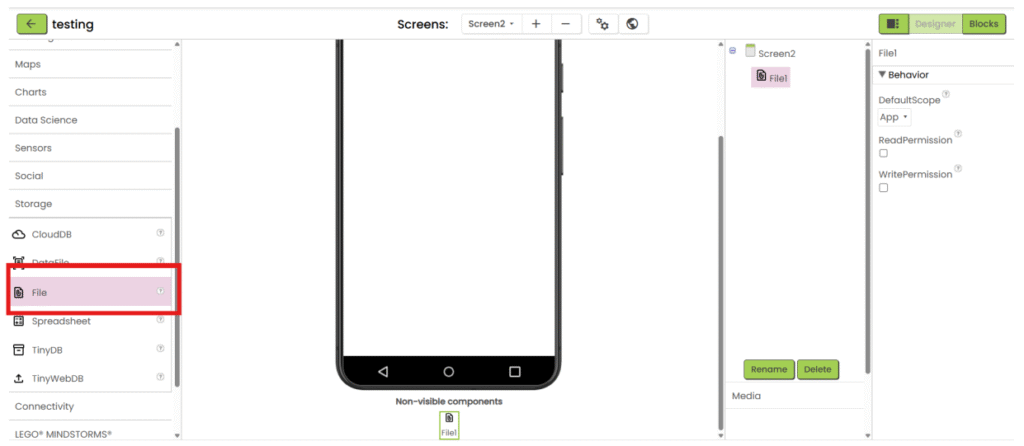
2. Add “File” component under “Storage” category.
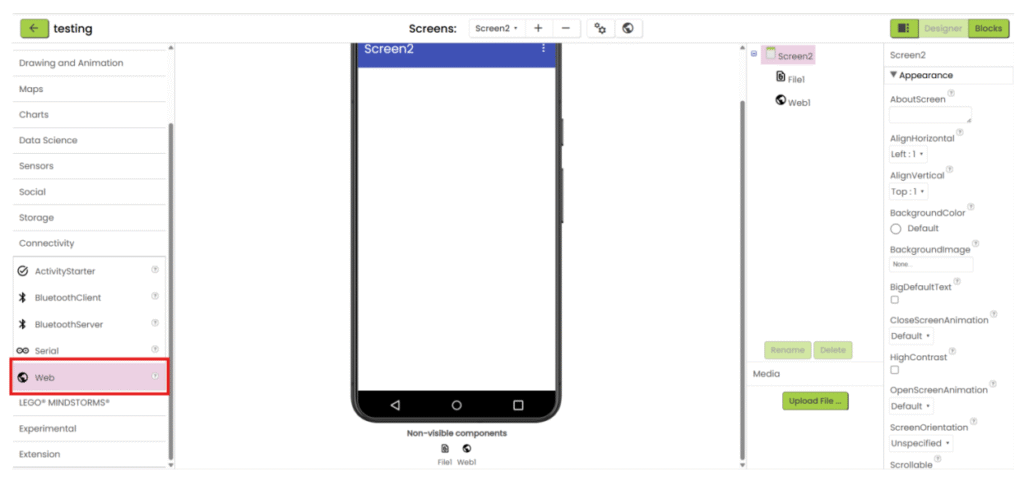
3. Add “Web” component under “Connectivity” category.
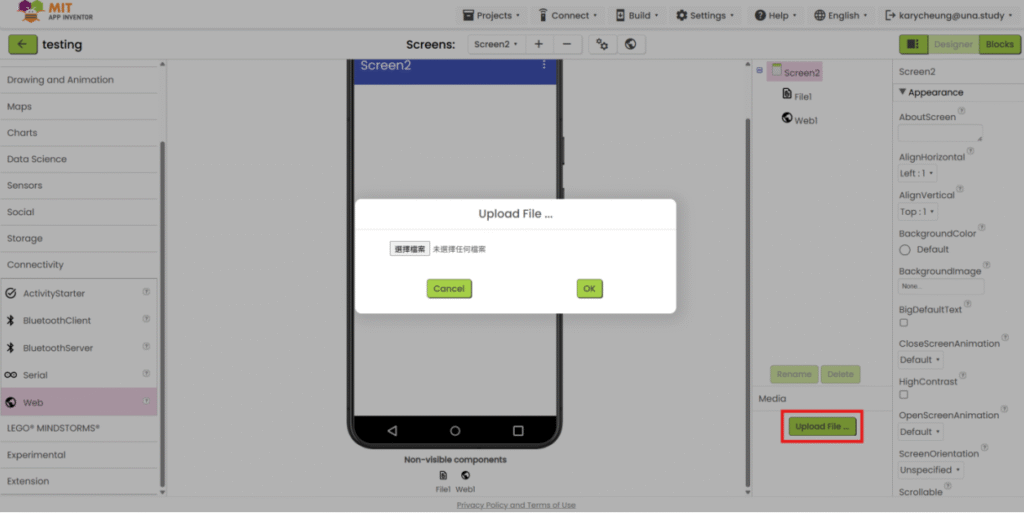
4. Upload the XML file.
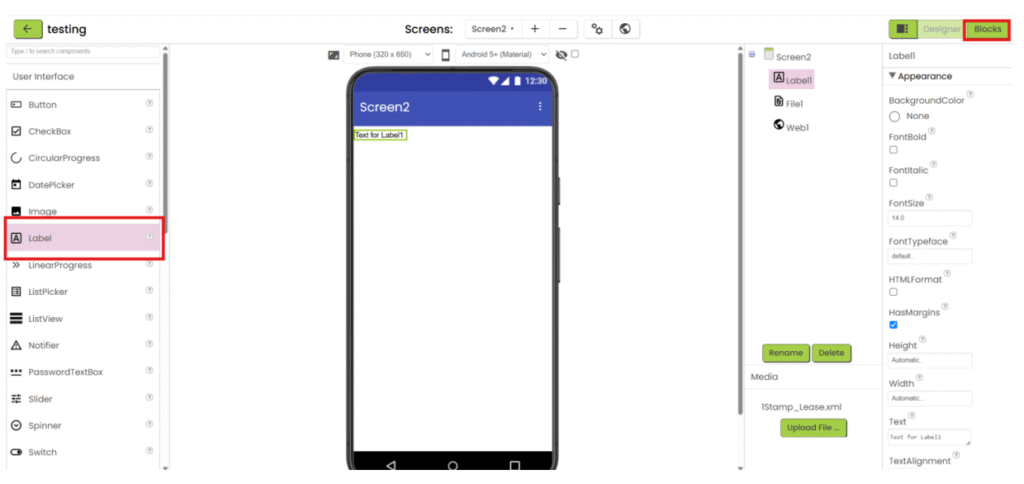
5. Add the necessary user interface component to show the data. Then go the “Blocks”.
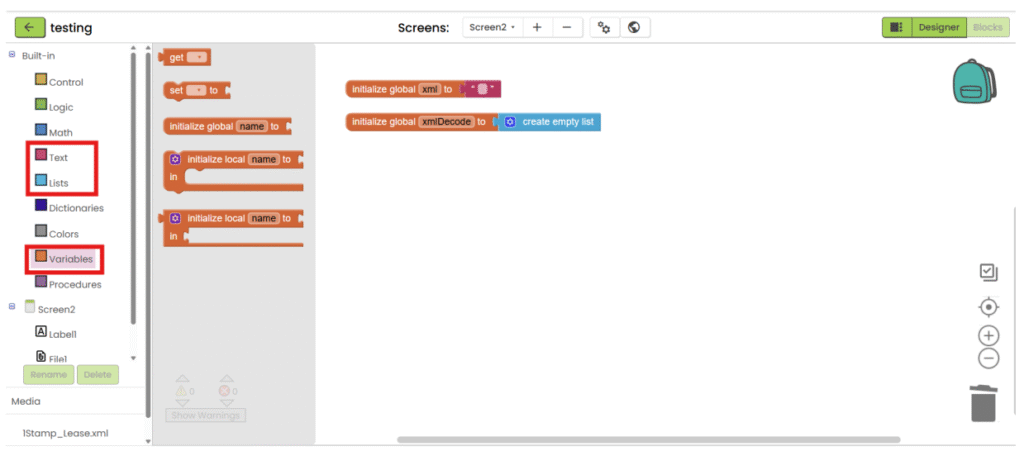
6. Create two variables. One for storing XML’s text (empty text), another one for storing decoded text (empty list).
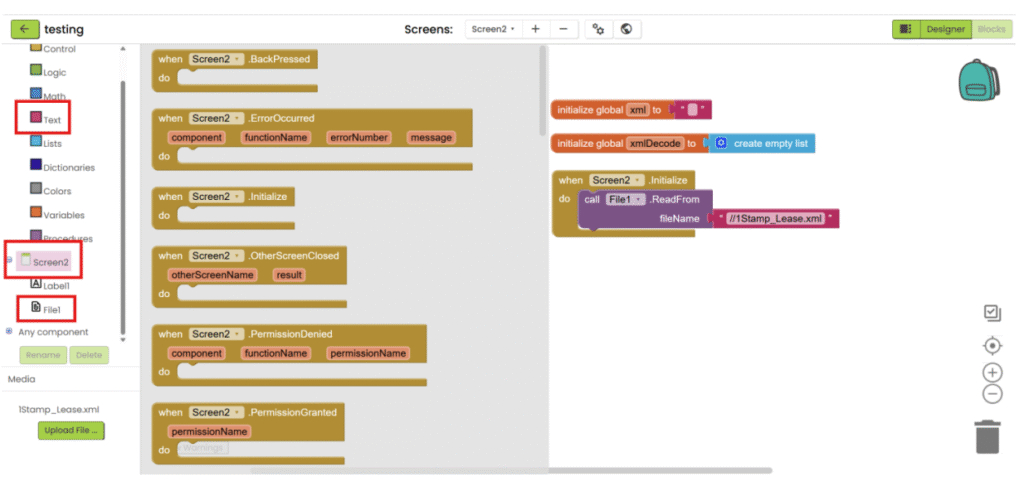
7. When screen is initialized, read the xml file. To read the xml file, you need to add “//” in front of the file name.
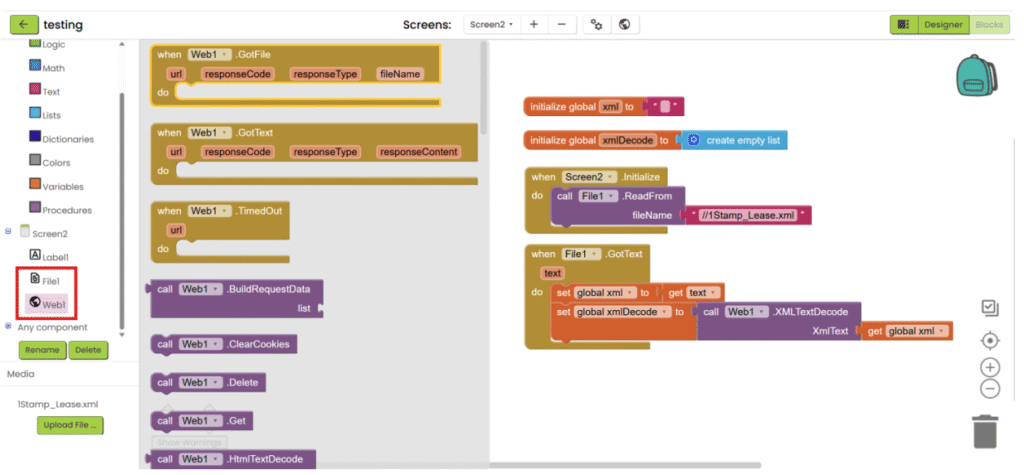
8. After the file is loaded, save the text, decode it and save it into variable.
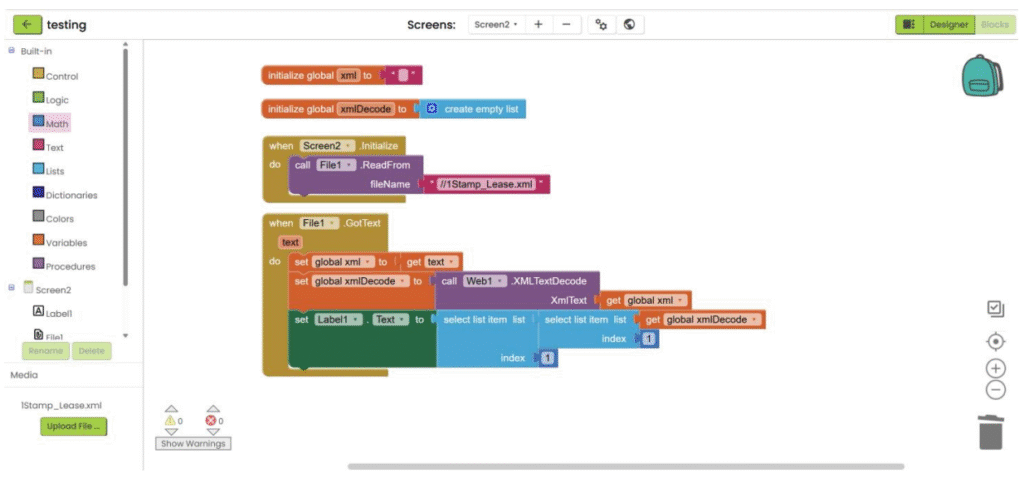
9. Get the targeted data with block in “Lists” category.
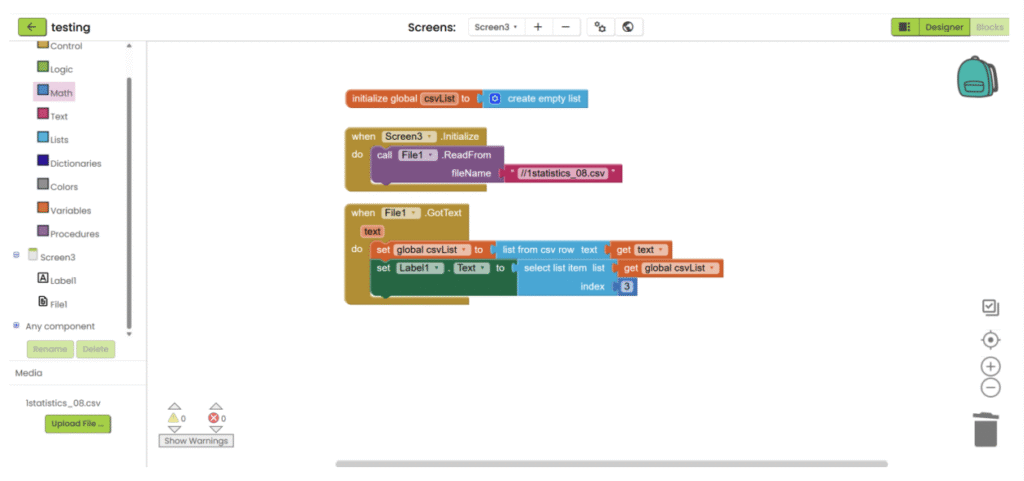
App Inventor with CSV
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-cr-crdata-stat-company-searches
1. Refer to steps 1-5 in “App inventor with XML”. Add “File” component under “Storage” category, upload the csv file and add the necessary user interface component to show the data. Then go the “Blocks”.
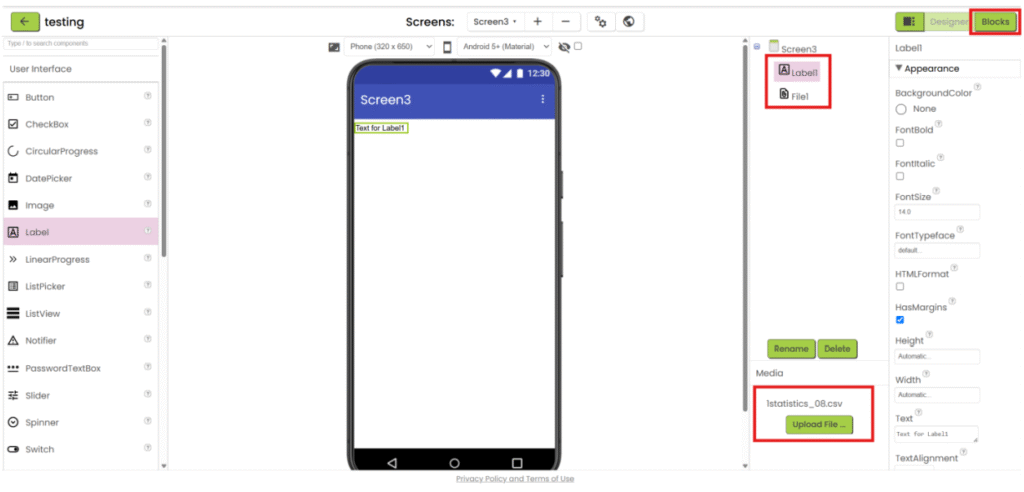
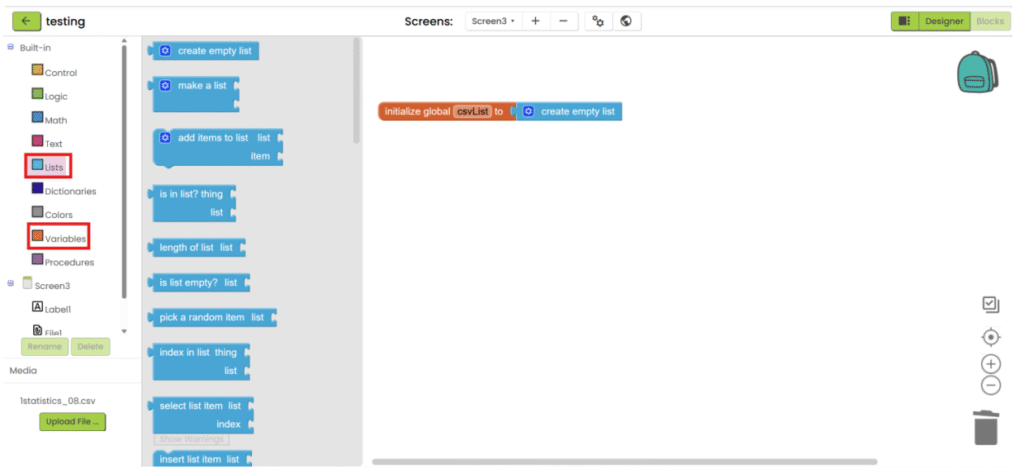
2. Create a variable for storing decoded text (empty list).
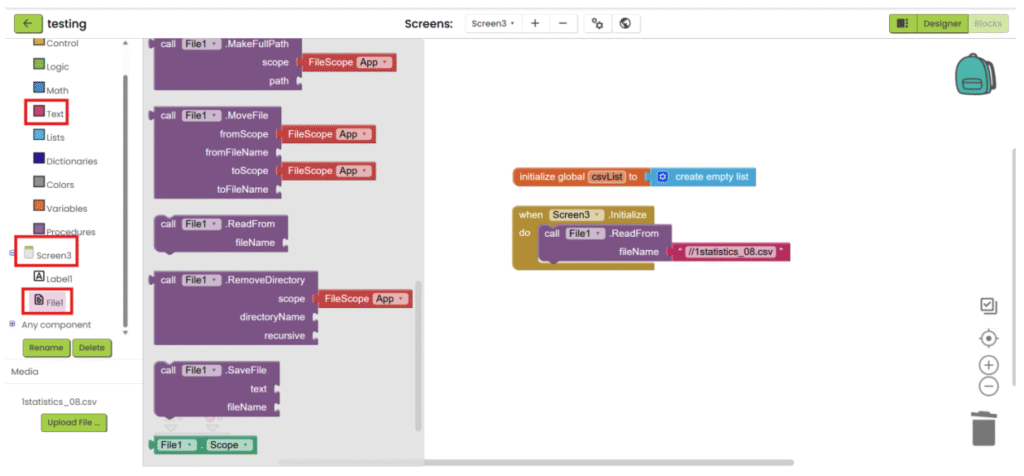
3. When screen is initialized, read the csv file. To read the csv file, you need to add “//” in front of the file name.
4. After the file is loaded, save the text, decode it and save it into variable.
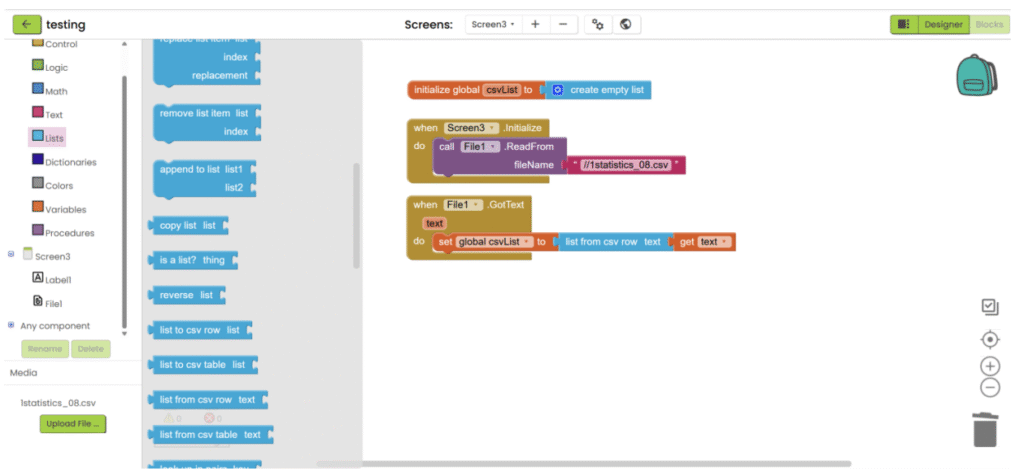
5. Get the targeted data with block in “Lists” category.
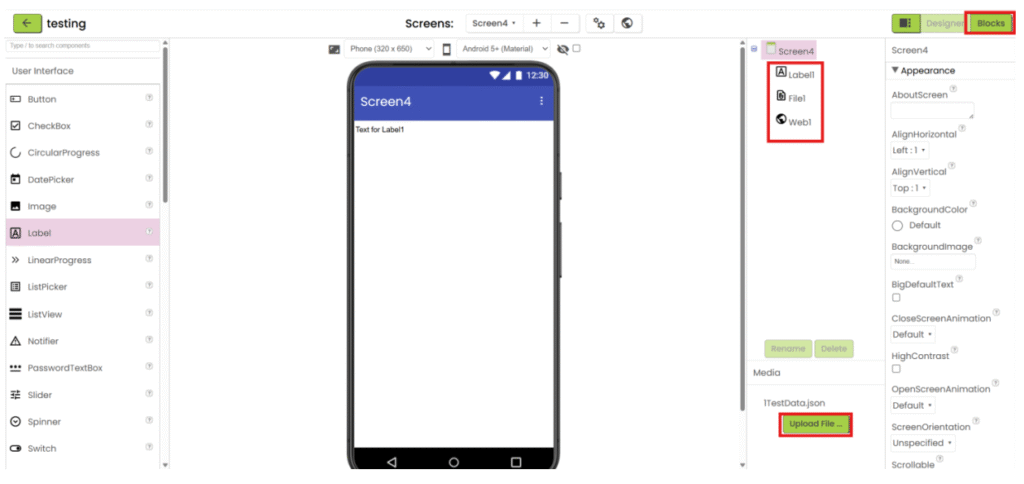
App Inventor with JSON
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-try-trymthfinr-press-release-financial-results
1. Refer to steps 1-5 in “App inventor with XML”. Add “File” component under “Storage” category and add “Web” component under “Connectivity” category. Upload the json file and add the necessary user interface component to show the data. Then go the “Blocks”.
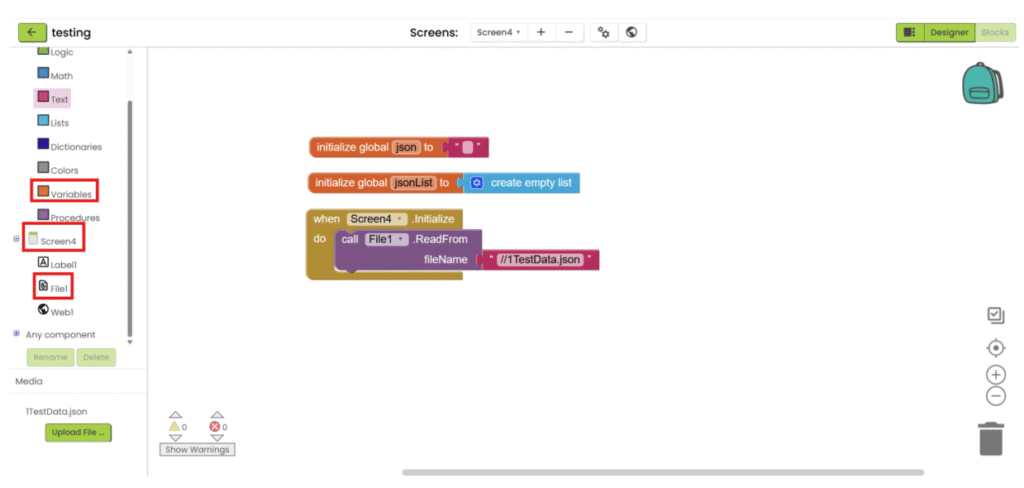
2. Create two variables. One for storing JSON’s text (empty text), another one for storing decoded text (empty list). When screen is initialized, read the json file. To read the json file, you need to add “//” in front of the file name.
3. After the file is loaded, save the text, decode it and save it into variables.
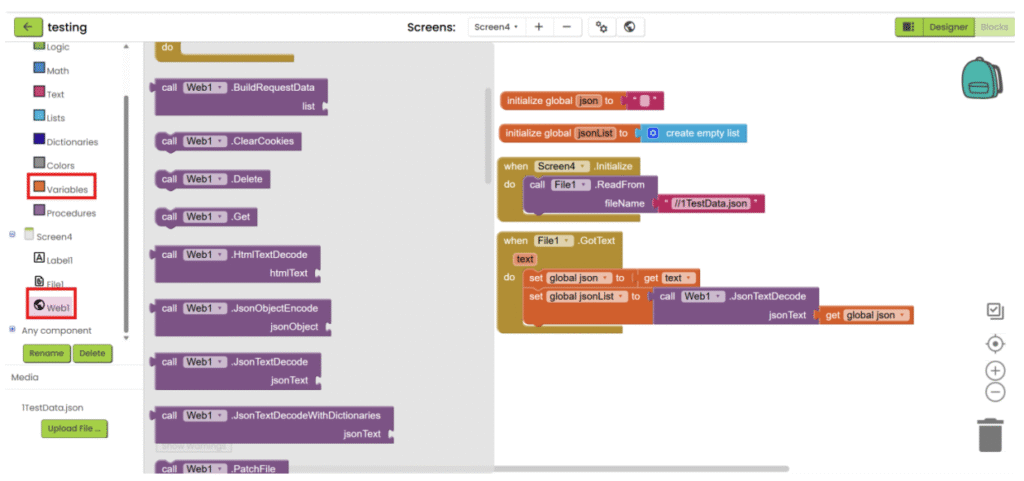
4. Get the targeted data with block in “Lists” category and “Dictionaries” category.
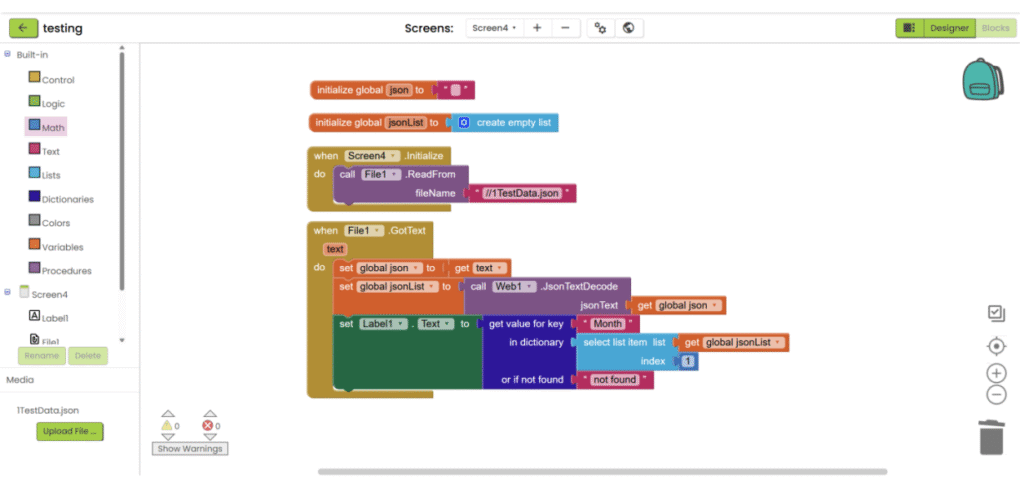
App inventor with API in JSON format
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-hkma-t03-t031203ch-statistics-turnover-fps-hkdpayment-vol
1. Refer to the steps 1-5 in “App inventor with XML”. Add “Web” component under “Connectivity” category and add the necessary user interface component to show the data. Then go the “Blocks”.
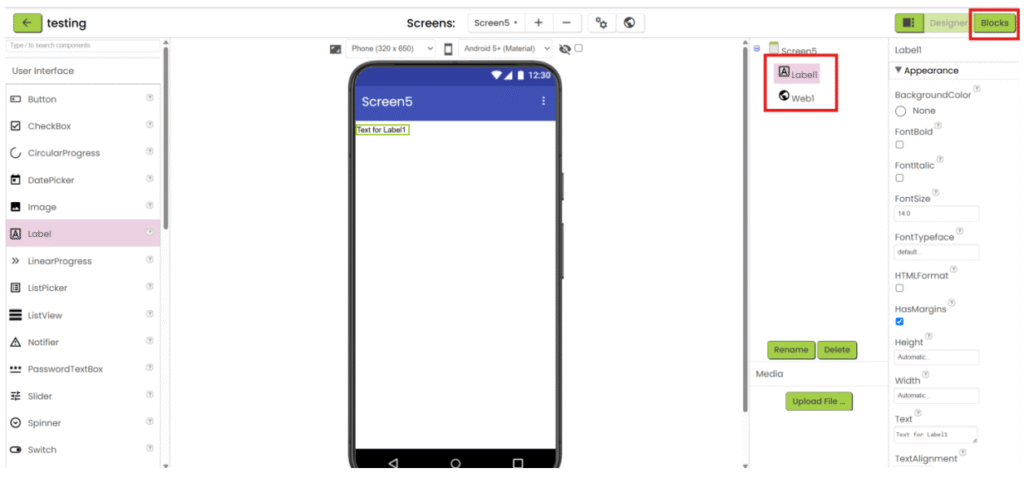
2. Create a variable for storing decoded text (empty list). When screen is initialized, set the URL of web
component and call the website.
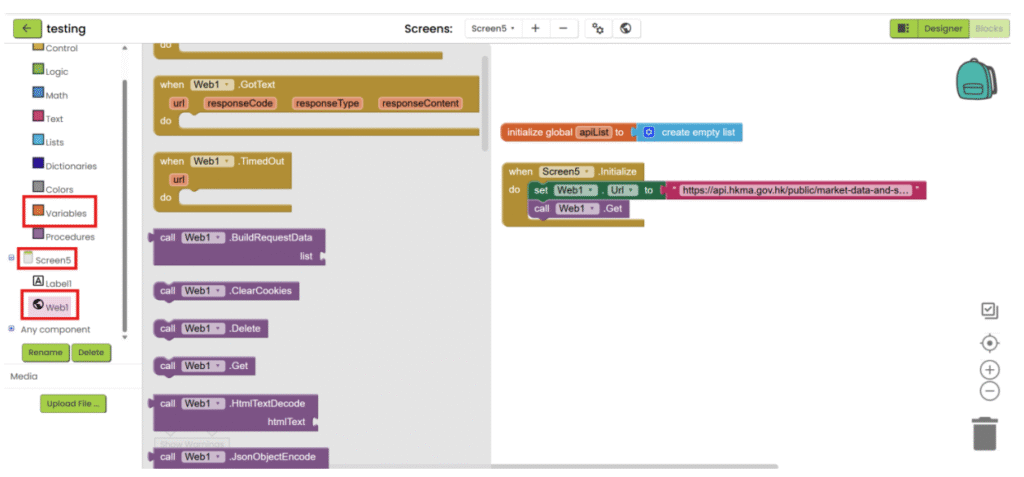
3. After the file is loaded, save the text, decode it and save it into variable.
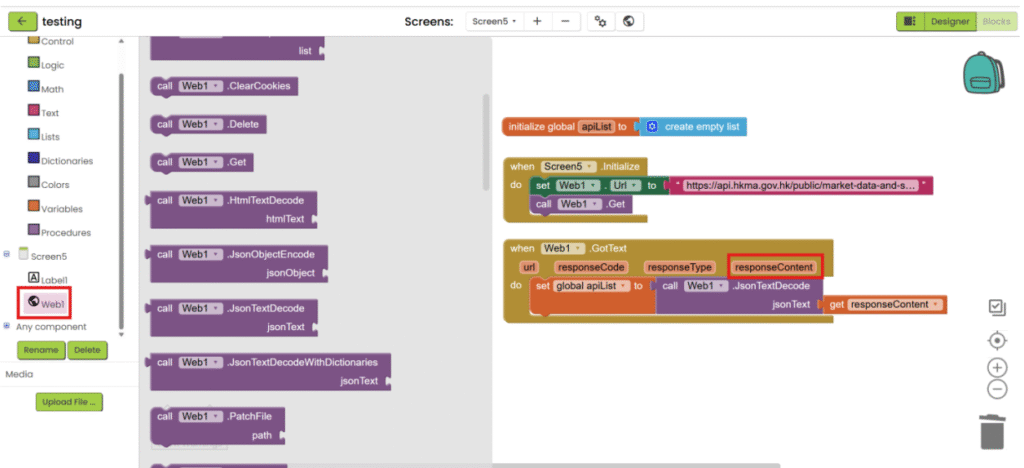
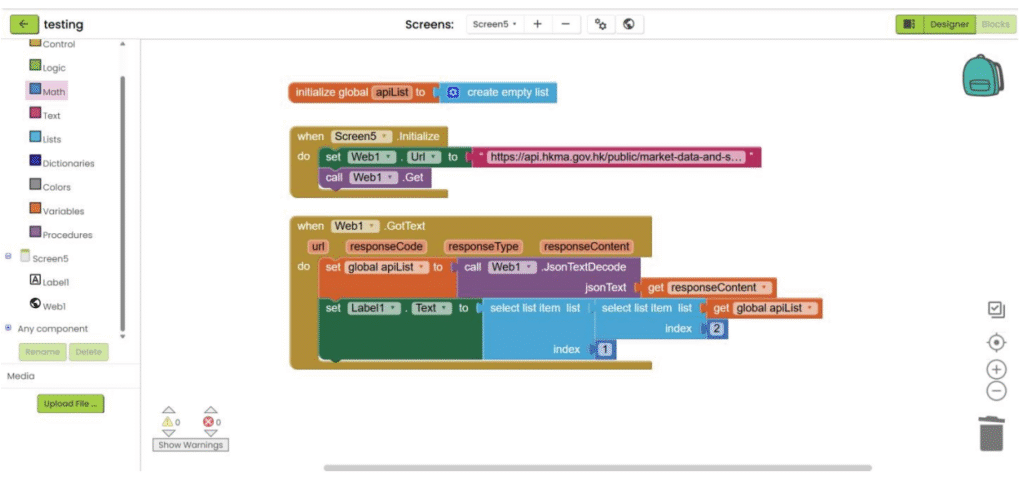
4. Get the targeted data with block in “Lists” category.
Python
Python with XML
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-ird-ird_json-stamp-lease

(stamp_lease.xml)
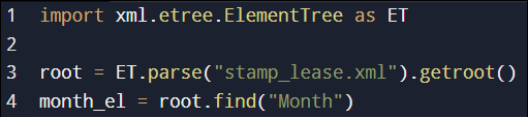
1. Create a project folder (e.g., python-data-reading) and put stamp_lease.xml inside it.
2. Use the built-in XML library: xml.etree.ElementTree (no extra installs needed).

3. Create variables to hold parsed elements and read the XML file from disk.
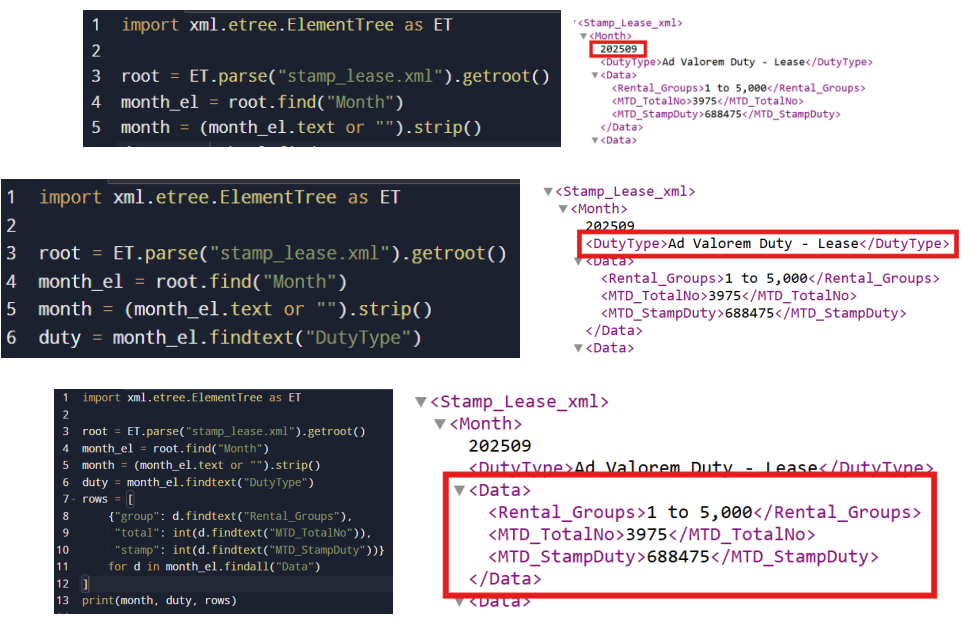
4. Parse and extract the targeted elements.
Python with CSV
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-cr-crdata-stat-company-searches
1. Use either built-in csv or pandas. (Built-in is simplest and needs no installation.)
2. Place image_records.csv in your project folder.

3. Create a variable (list) to store rows.

4. Open and read the CSV file. Decode and save rows into variables (dicts or lists) and print the result.

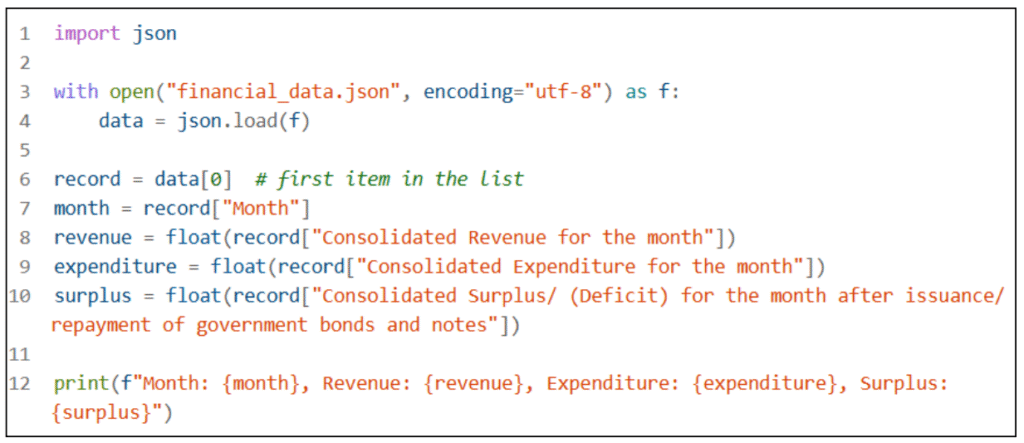
Python with JSON
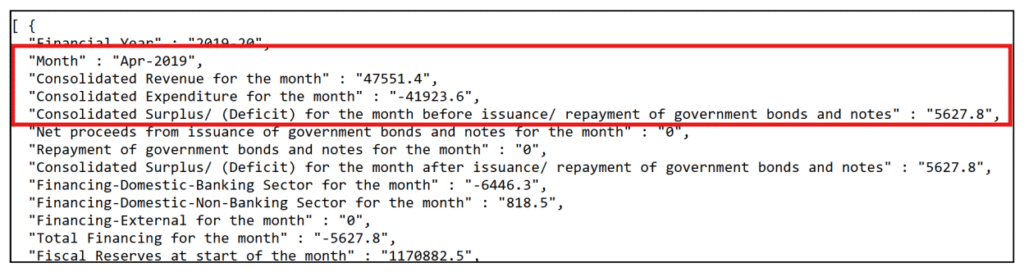
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-try-trymthfinr-press-release-financial-results
1. Place financial_data.json in the project folder.
2. Use Python’s built-in json module.

3. Create variables to hold the parsed dict/list. Read and load the file into a Python dict.

4. Extract targeted data and display or process the values.
Python with API in JSON format
Data used: https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-hkma-t03-t031203ch-statistics-turnover-fps-hkdpayment-vol
1. Install requests if needed: pip install requests.

2. Import requests and call the API with GET.

3. Check response status and decode JSON and save the decoded JSON to variables (dict/list).
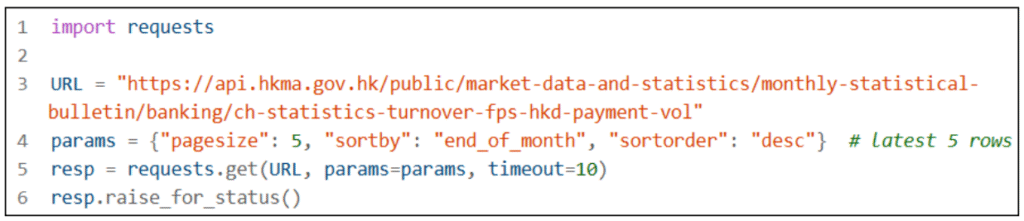
4. Extract targeted fields as needed.

JavaScript
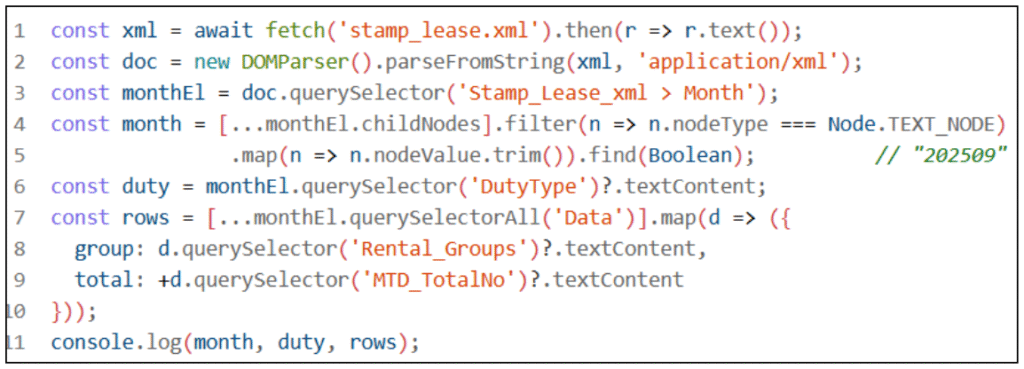
JavaScript with XML
1. Use fetch() to load the XML file.
2. Put stamp_lease.xml in the same folder as your HTML/JS.

3. Parse with DOMParser(‘application/xml’).

4. Read the month text from (mixed content: text + child nodes).

5. Extract and iterate each block to get fields. Display the data (console or UI).
JavaScript with CSV
1. fetch() the file and read as text.
2. Put image_records.csv in the same folder.

3. Split by newline to get rows; split the header to get column names.

4. Map each row to an object; coerce numbers where needed. Display or bind to UI.

JavaScript with JSON
1. Put financial_data.json in the same folder.
2. fetch() and response.json() to parse.

3. Read the first record (index 0).

4. Convert number-like strings with unary + or Number(). Display or compute.

JavaScript with API in JSON format
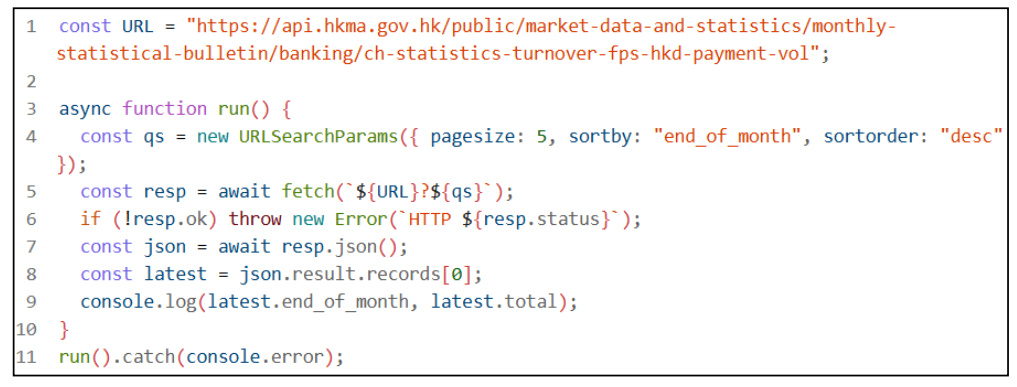
1. Build query params (e.g., latest 5 rows sorted by end_of_month desc).

2. fetch() the URL + params.

3. Check resp.ok, parse JSON, read result.records.
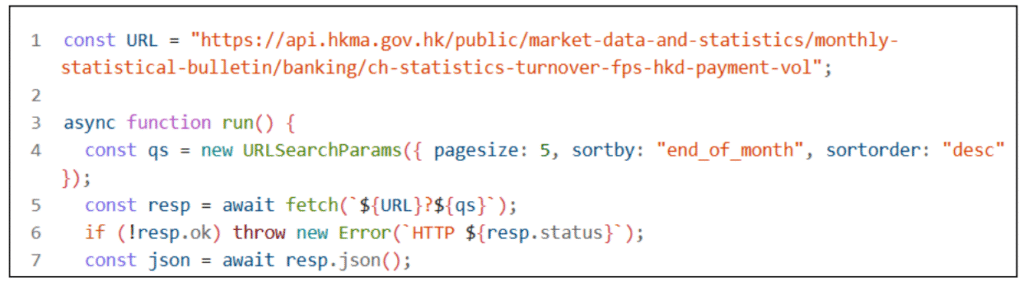
4. Use the latest row and print end_of_month + total.